Requirements
Queries in jAgE must fullfil following requirements:
- Simplicity of both defining of a query and its execution.
- Reusability of a single query against many targets.
- Good performance of execution.
- Extensibility — to allow creation of problem-centric queries.
On this page:
Implementation
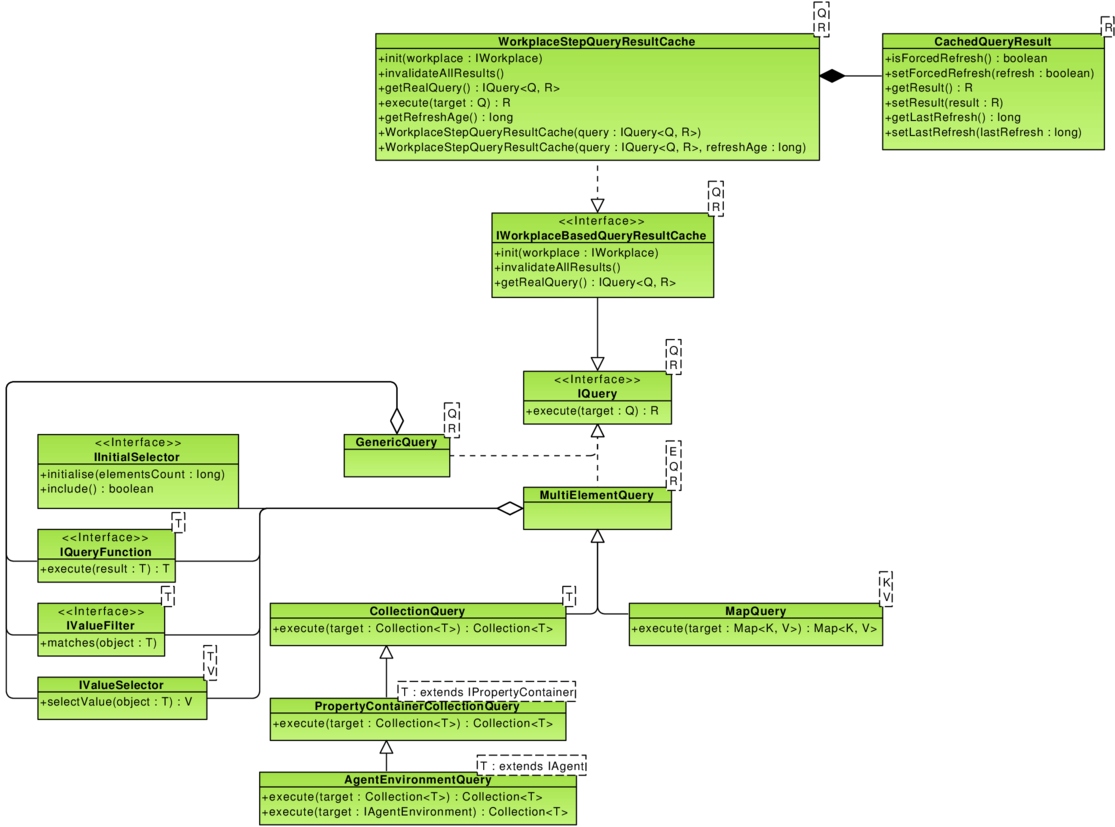
The queries mechanism is centered around the IQuery interface. It represents a query and declares only one operation: R execute(Q target) where:
- R is a type of the result of the query.
- T is a type of a queried object.
The platform offers a mechanism to build queries using a semi-fluent interface. This mechanism is implemented in the GenericQuery class and its subclasses. Three operations for declaring a query are defined:
- Initial selection, represented by
IInitialSelector: performs preselection of the values to query. - Filtering by value, represented by
IValueFilter: similar toWHEREclause in SQL. - Selection of values (e.g. fields from objects): similar to
SELECT x, yfrom SQL. - Functions, represented by
IQueryFunction: operations working on an entire result set, can remove, add or modify elements.
The execute() method of all subcless of MultiElementQuery works in the following sequence:
- Execution of initial selectors in the order they were added to the query. This means that all selectors must match for an element to be included in following actions.
- Matching of values with value filters. Consecutively added value filters are joined with the AND operator.
- Selection of the apropriate values. This step is omitted if no
IValueSelectorwas added. In this case full objects are used. - Execution of functions in the order they were added.
In the case of GenericQuery the first phase is omitted.
Following specialised query classes are provided out-of-the-box with the platform:
MapQueryfor querying all implementations of thejava.util.Mapinterface. Results are always a map.CollectionQueryfor querying all implementations of thejava.util.Collectioninterface. Results are always a collection.PropertyContainerCollectionQuerythat is aCollectionQuerywith some additional methods to match contents of property containers.AgentEnvironmentQuerythat allows transparent querying of agent environments.
Cache
In the version 2.5 only a simple cache based on the workplace step is provided. To work it needs to have an access to the workplace with the step property. It is not a general solution and it has a reduced application.
For the example usage of the cache see Queries.
When implementing a new cache you should consider following aspects:
- A cache should work as a proxy for a query (if it is a cache for results). It allows to transparently replace queries with cache in already existing classes.
- Provide a way to invalidate cached results.
- Use already existing envelope for cached results:
CachedQueryResult.